Arduino Car Proyect
How to build a car with arduino that detects obstacles
- Introduction
- Materials
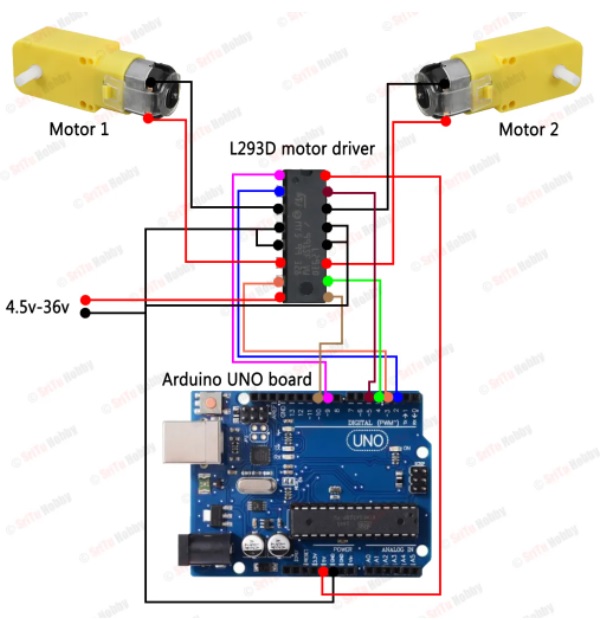
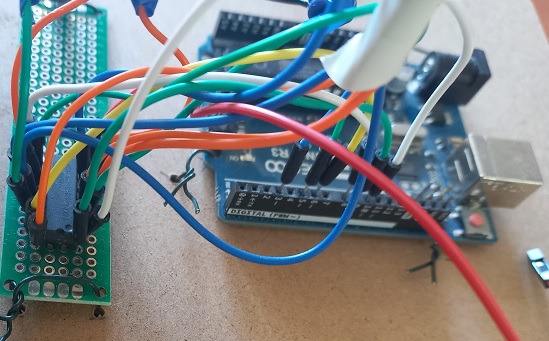
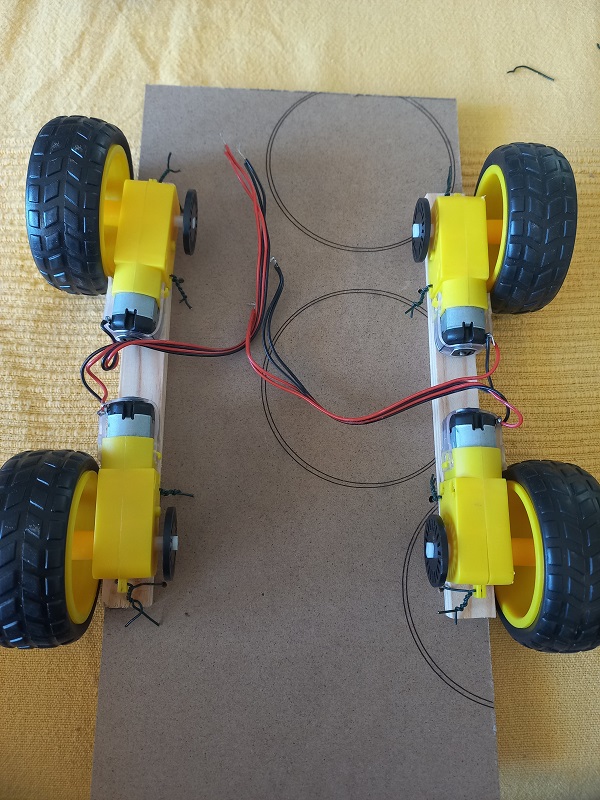
- Connect the motor controller, Arduino and the motors.
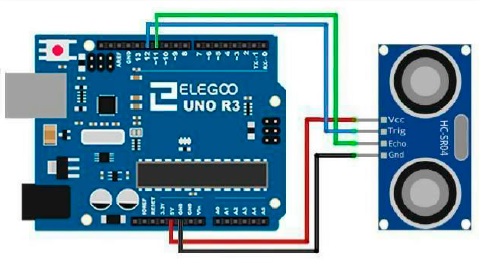
- Connect the ultrasounds Sensor to arduino
- Assembling the components
- Program Arduino
- Congratulations !!!
Tip: Get fun!!
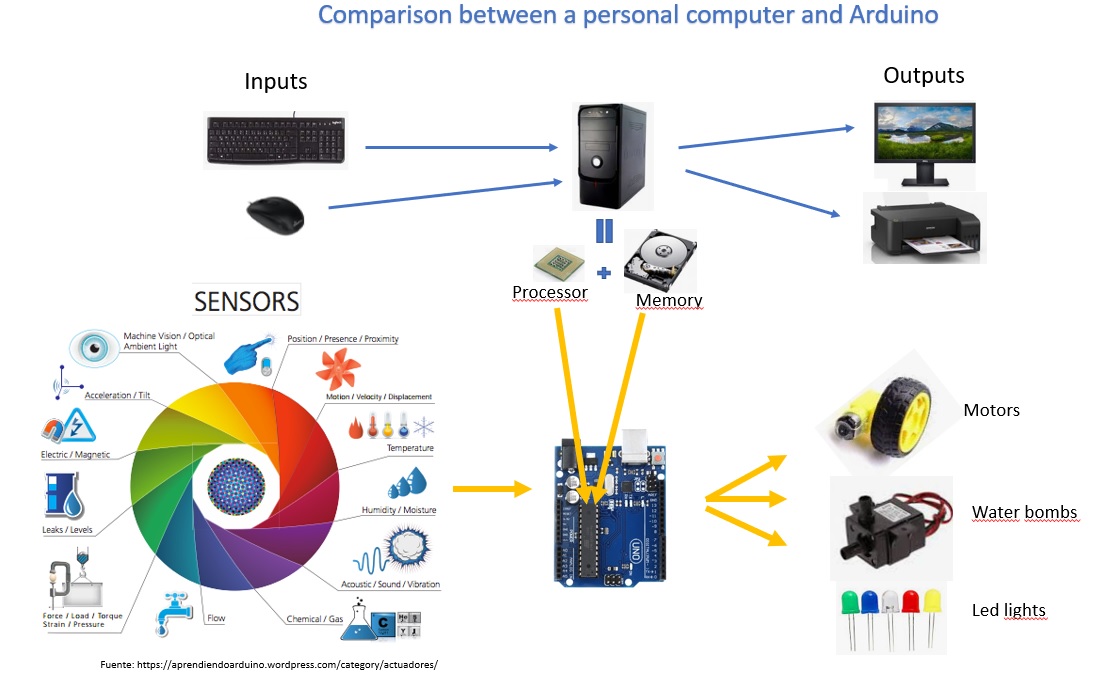
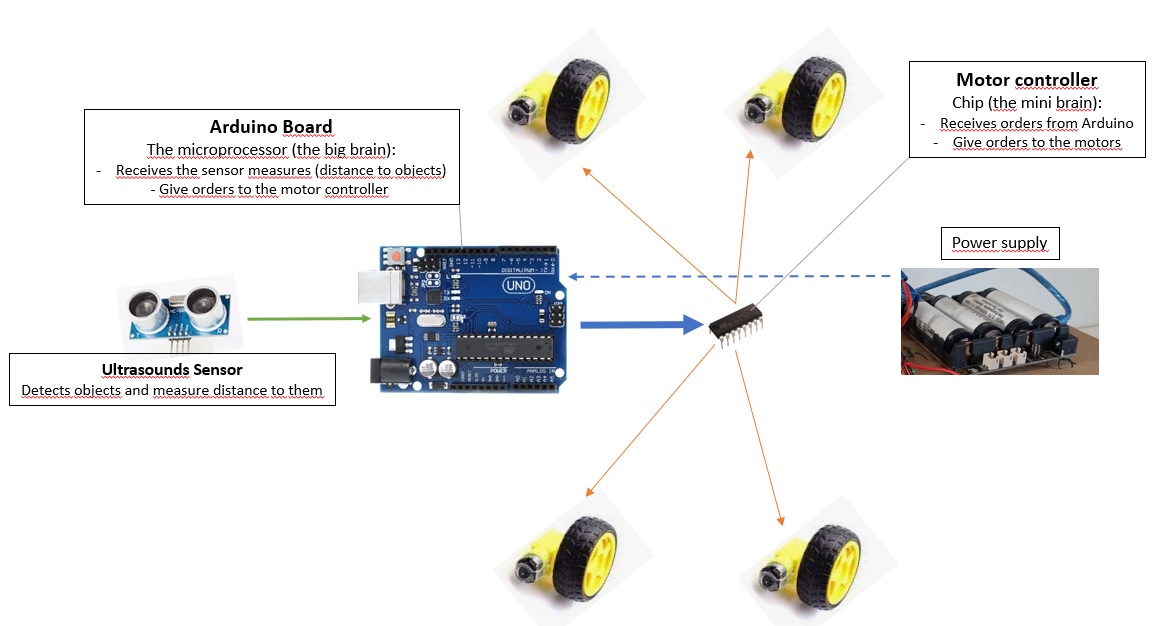
- Ultrasounds Sensor gives the distances of objects in front of the car
- The microprocessor (Arduino) receives the distances from the sensor:
- If there is no object continues moving forward
- If there is an object in front turns left to avoid it
- The microprocessor (Arduino) gives the order to motor controller and the controller order to the wheels to move
Important: Watch the car in action!!
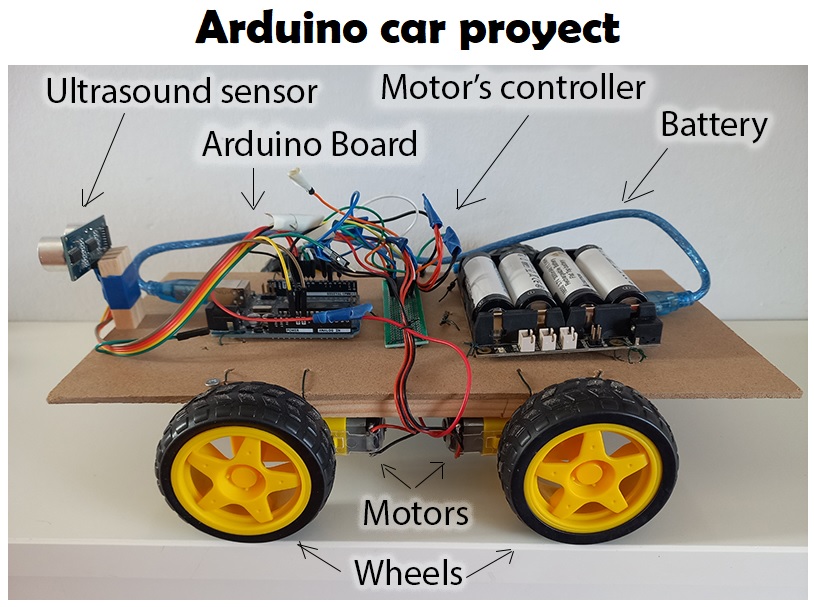
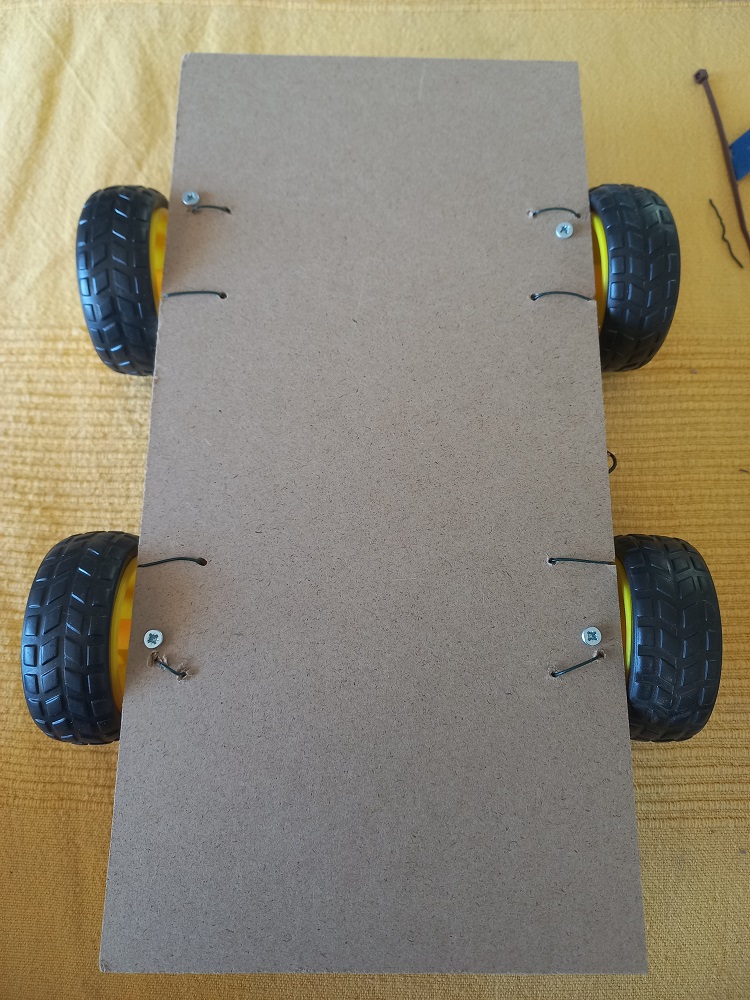
Materials
- Arduino UNO R3 - basic kit : 23.99 €

- Wheels and motors kit : 21.00 €

- DC motor controller (L293D): 1.60 €

- Electrical insulation tape

- Ultrasounds Sensor HC-SR04 - 2.70 €

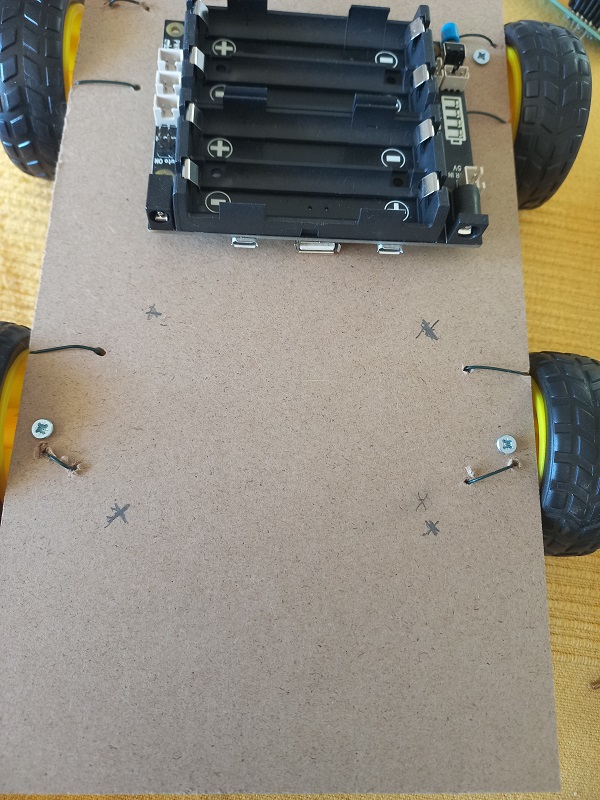
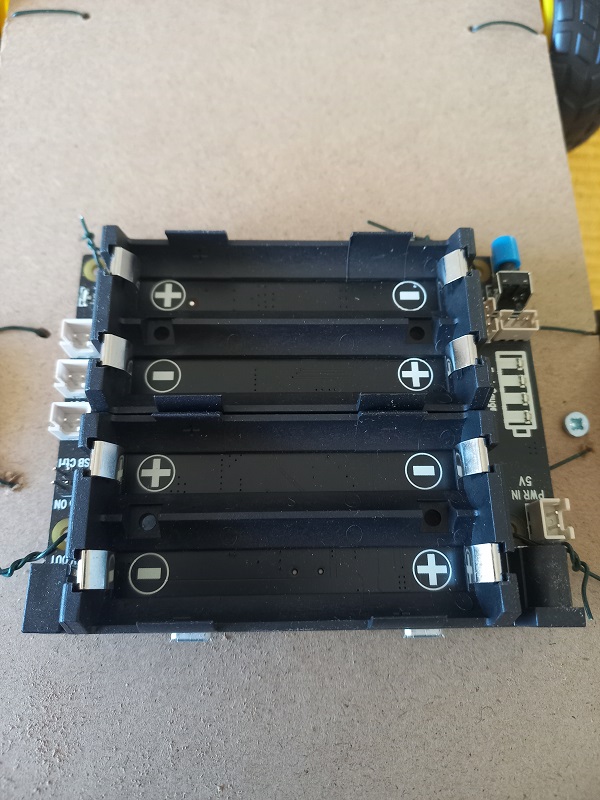
- 5 V Power Supply
- Chipboard sheets for crafts : 7.37 €

- PC with Arudino IDE installed

- Attach the power bank
- Attach the motor controller
- Attach Arduino UNO microcontroller board
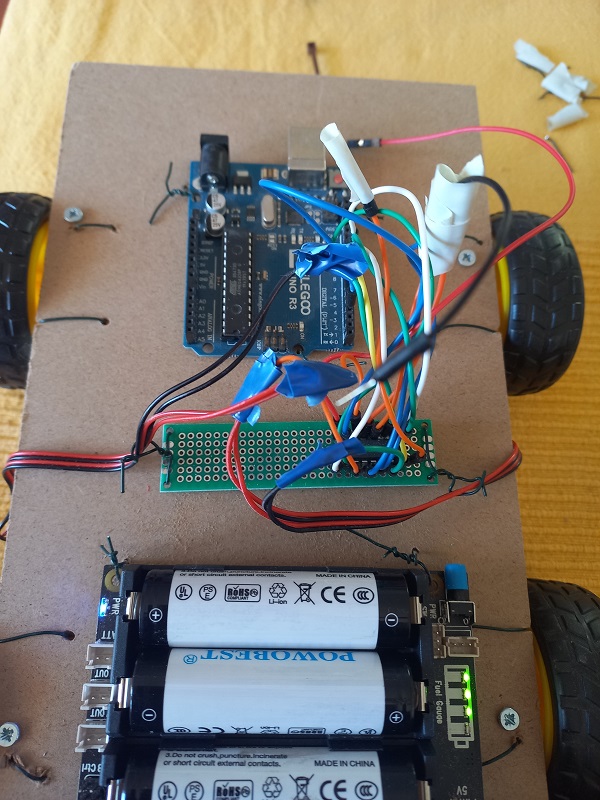
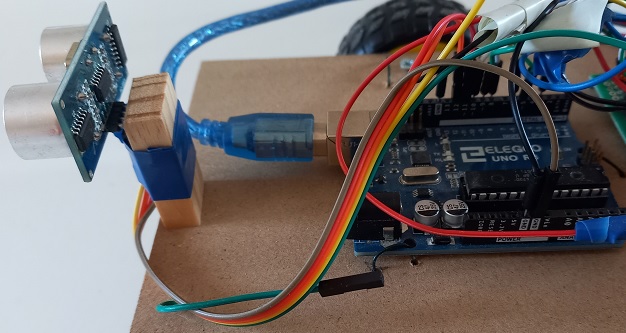
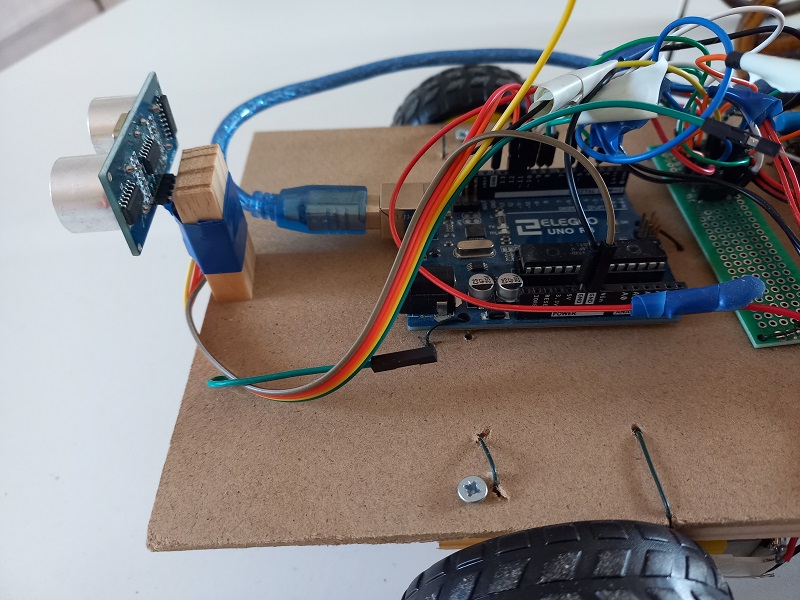
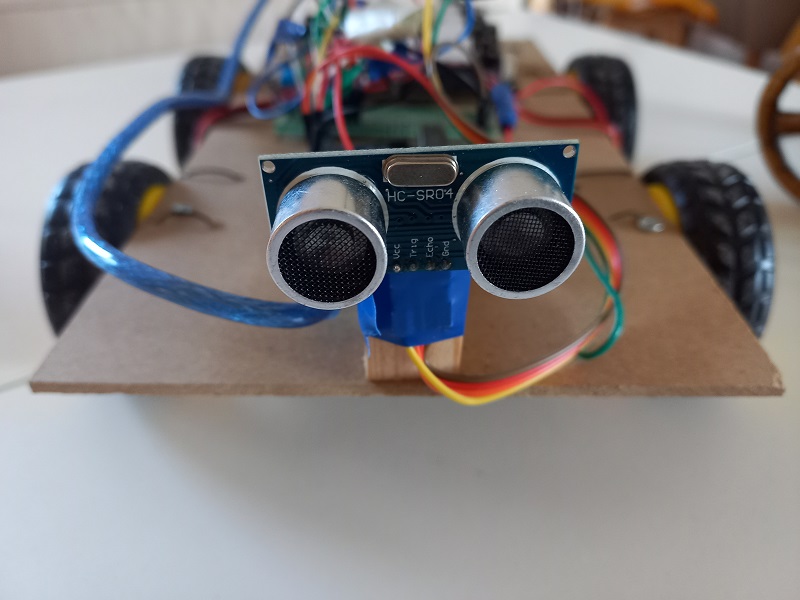
- Attach the ultrasounds Sensor in front of the car
Programming basics:
The computer executes instructions one after the other. I1 -> I2 -> I3 ....
Each instruction ends with ";"
To store information use:
- Constants: its value does not change (for example: const int pinIqda = 9;)
- Variables: its value changes over the time (for example: int distancia=0; distancia= distancia + 2 )
There are two main parts (funtions) in Arduino:
- Setup(): it runs only once at start
- Loop(): it repeats endlessly
Use "//" to write comments in the code Use "{ }" to build a set of instructions
Control the program flow: IF

Other usefull functions:
- pinMode (1, OUTPUT) or pinMode (1, INPUT) : sets a arduino pin to receive inputs o give outputs
- analogWrite or digitalWrite: sends information throught pins
- Serial.print : writes something in the monitor
- delay(1000) : makes the program to wait 1000 miliseconds.
Now, write the code in Arduino IDE.
- Check if the code is ok: press

-
Conect Ardunio and the computer with USB
-
Transfer the code to Arduino: press

NewPing sonar(12,11, 200); // Pin 12 and 11 for the ultrasonic sensor and with a maximum distance of 200cm
const int pinIqda = 9;
const int pinDcha = 10;
const int pinIqdaAdelante = 8;
const int pinIqdaAtras = 3;
const int pinDchaAdelante = 6;
const int pinDchaAtras= 5;
int distancia=0;
void setup() // initial instructions
{
// configure arduino pins
pinMode(pinIqda , OUTPUT);
analogWrite(pinIqda, 254); // left speed, set up to max
pinMode(pinDcha , OUTPUT);
analogWrite(pinDcha, 254); // right speed, set up to max
pinMode(pinIqdaAdelante , OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinIqdaAtras , OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinDchaAdelante , OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinDchaAtras , OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600); // show ping meassures
// start the engines
digitalWrite(pinIqdaAdelante ,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinIqdaAtras , LOW );
digitalWrite(pinDchaAdelante , HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinDchaAtras ,LOW);
}
void loop() // Instructions that repeat themselves endlessly
{
delay(1000); // wait 1000 miliseconds between ping
distancia=sonar.ping()/ US_ROUNDTRIP_CM;
Serial.print("Ping: ");
Serial.print(distancia); //
Serial.println("cm");
if (distancia>2 && distancia<50 ) { // turn left
digitalWrite(pinIqdaAdelante ,LOW);
digitalWrite(pinIqdaAtras, HIGH );
digitalWrite(pinDchaAdelante , HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinDchaAtras , LOW);
delay(3000); // wait 3 iseconds to turn left
}
if (distancia>=50 ){ // go forward
digitalWrite(pinIqdaAdelante ,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinIqdaAtras , LOW );
digitalWrite(pinDchaAdelante , HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinDchaAtras ,LOW);
}
}